Japan is a traditional country, and many businesses have been in the family for many, many generations. Some establishments have been in operation for over 1000 years. In this article, we are going to talk about these traditional businesses that have been given the name of Shinise.
Shinise is a Japanese phenomenon referring to companies that were founded many years ago, usually before World War II. They tend to be very old but are still operating, sometimes after several generations.
Throughout history, old companies have been recognized for their reliability in carrying out their traditional businesses, but we can also observe a trend that their management models tend to be conservative.
These old companies are usually in traditional sectors, such as beverage, sweets and Japanese biscuit manufacturing. Others are restaurants, hotels, department stores and other types of fabrications.
We also recommend reading:
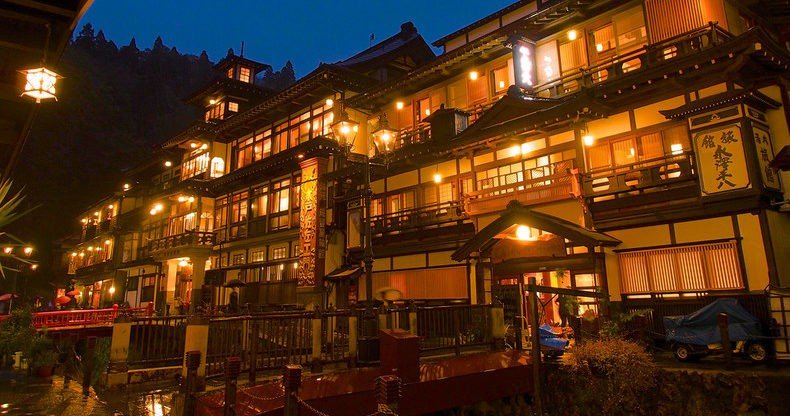
- Ryokan - The charming Japanese inns
- Imperial Japan History - World War II and Fall
- Kimono - All about traditional Japanese clothing

Índice de Conteúdo
The importance of long-standing establishments
Long standing businesses are very important to Japan as they are a testament to the country's history and culture. In addition to having great symbolic value, these businesses represent the longevity, stability and resistance of the Japanese over the centuries.
During the Heisei recession, we saw rapid growth of businesses catering to the needs of end consumers such as niche markets. Such companies have survived by offering superior services and products to the Japanese people.
According to data from 2007, there are more than 21,000 companies in Japan with more than 100 years of foundation, and more than 3,000 with more than 200 years. In 2017, that number rose to 33,069 companies.
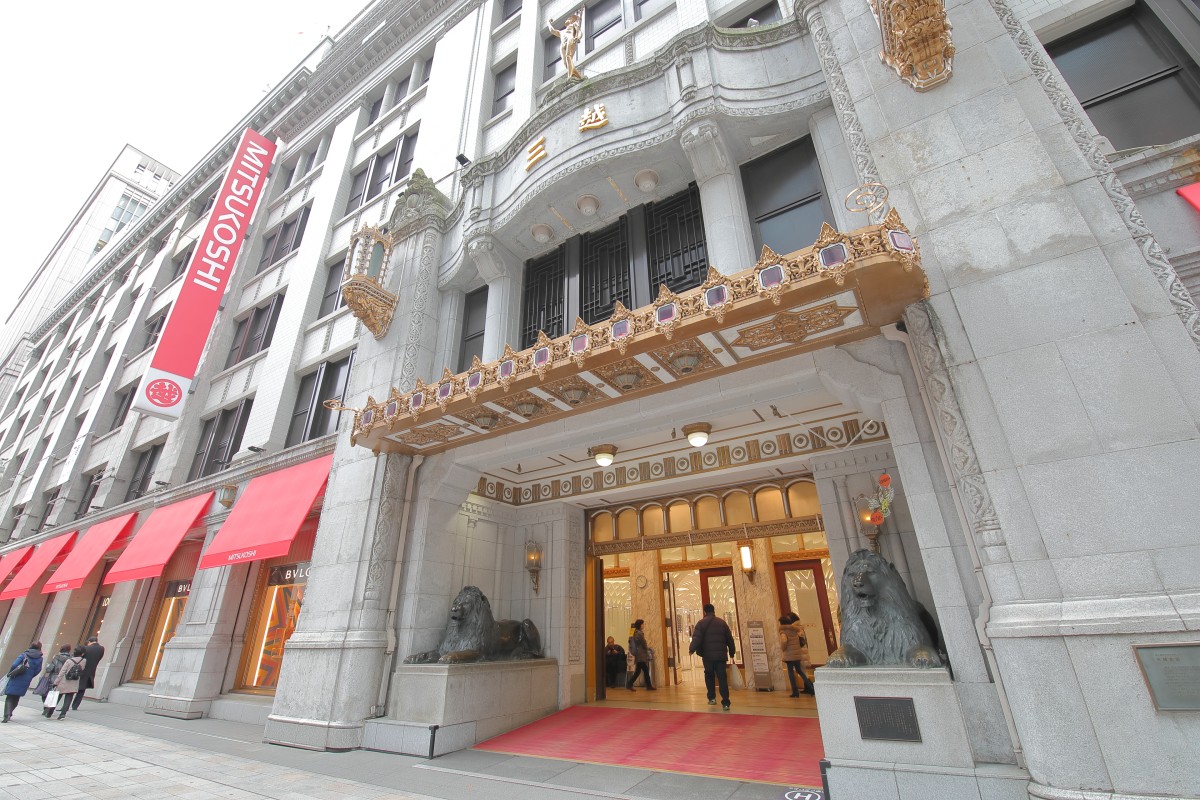
It is common to find kimono shops founded since the Edo era, but many of them have grown into large stores and are still in business today.
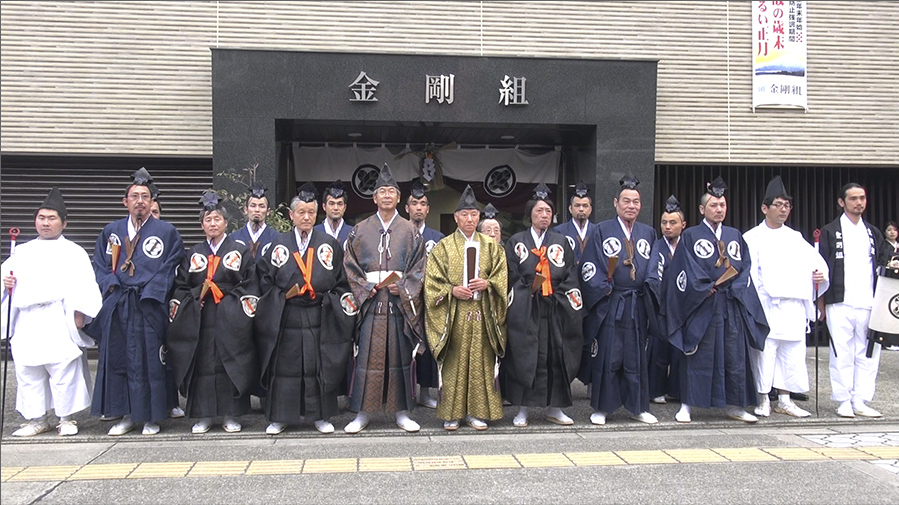
The best-known example of old stores that originated as kimono stores is Mitsukoshi stores (founded in 1673). The oldest store in Japan is an Osaka construction company Kongo-gumi founded in the year 578.
One of the requirements for a company to be called Shinise is to have been in business for over 100 years. It is very likely that over the centuries, some businesses over 100 years old had their doors closed, but this is very difficult to calculate.

What does Shinise mean?老舗]
"Shinise" (老舗) is a Japanese word meaning "old shop" or "traditional establishment". A good way to translate it would be "A long standing store".
It can refer to a store or business that has been in business for many generations, with a long history and tradition. The word can also refer to an establishment that maintains a traditional look and feel.
Sometimes the term can encompass pioneering organizations being in different businesses, even if they do not follow the same original branch, as in the case of Nintendo, which started out making Hanafuda decks, and then moved into the video game business.
Read also: Nintendo Character Names in Japanese – Mario and Smash
What makes a business last for generations?
There are several factors that can lead to a business lasting for generations and generations. Some of these factors include:
- High quality products or services: maintaining high quality standards in your products or services can help you retain loyal customers and attract new customers.
- Innovation: being able to adapt to changes and changes in the market and trends can help keep the business competitive and relevant.
- Strong Leadership: Strong, visionary leaders can help guide the business through challenges and opportunities.
- Strong values: maintaining strong values and a solid company culture can help maintain unity and commitment within the company.
- Financial planning: having good financial management, including saving for times of economic difficulty, can help keep the business stable.
- Familiarity with Tradition: keeping ancient traditions and techniques but adapting them to the modern world can help maintain the company's identity.
- Family succession: Passing the business down from generation to generation is common practice in Japan and can help maintain business continuity and stability.
- History and tradition: Japan has a rich history and a strong tradition of crafts and handicrafts, passed down from generation to generation. Many of these old companies are still dedicated to these old traditions and techniques.
- Cultural values: Japanese culture values stability, loyalty and continuity, which can be seen as an advantage for companies that last for generations.
- Government protection: the Japanese government has policies and programs to support and protect legacy companies.
- Religious beliefs: The Japanese believe that ancestors and ancestor spirits are important and should be respected. This may have contributed to the belief that old businesses are sacred and must be maintained.

The article is still halfway through, but we recommend also reading:
1000 year old companies
This list is of companies founded more than 1000 years ago. These companies are commonly referred to as “1000-year companies” 「1000年企業」sennenkigyou.
According to a survey by Tokyo Shoko Research, there are currently 7 companies with a history of over 1000 years, plus two companies not listed in the survey, making a total of 9 companies:
- Kongo-gumi (金剛組), founded in 578, construction of wooden buildings, Osaka.
- Ikebukuro-Kado-kai, founded in 587, teaching tea ceremonies and art.
- Nishiyama Onsen Keiunkan, founded in 705, hospitality.
- Furuya, founded in 717, hospitality.
- Zenko-ro, founded in 718, hospitality.
- Tanaka Issey, founded in 889, manufacturing religious utensils.
- Nakamura Yakushi-ji, founded in 970, construction of wooden buildings.
- Sankan, founded in 1000, hospitality.
- Ichimonjiya Kazufusa, founded in the year 1000, restaurant.
There must be some other establishments with a history of more than 1000 years, including individual stores, in Japan and other countries.
However, it is important to note that some of these establishments with a history of over 1000 years may have changed ownership or significantly altered their commercial activities over the years, the list just shown shows businesses that have remained in the family or in the niche for generations.

Japan's Longest Running Business List
There are hundreds of companies that date back to 1800-1900 and are still in operation today, but we want to list the oldest ones that go back to before 1600.
Japanese candy factories
- 1000 (一文字屋和輔) Ichimonjiya Wasuke
- 1184 (藤戸饅頭本舗) Fujido Manjū honpo
- 1327 (紅蓮屋心月庵) Gōrenya Shinku an
- 1329 (かん袋) Kan fukuro
- 1333 (黒田千年堂) Kurōda Sennen dō
- 1349 (塩瀬総本家) Kan se Sōhonke
- 1421 (亀屋陸奥) Kameya Matsu ō
- 1461 (駿河屋) Suruga ya
- 1477 (水田玉雲堂) Mizuta Tamakudō
- 1502 (平戸蔦屋) Hirado Tsuta ya
- 1503 (川端道喜) Kawabata Dōki
- 1520 (虎屋) Tora ya
- 1532 (本家小嶋) Honke Kojima
- 1550 (笹井屋) Sasai ya
- 1562 (太田屋半右衛門) Ōta ya Hannyemon
- 1565 (太閤餅) Taiko mochi
- 1575 (柳屋奉善) Yanagi ya Hōzen
- 1576 (玉英堂) Gyokuyingado
- 1584 (五太夫きくや) Gotaifu Kikuyaya
- 1585 (本家菊屋) Honke Kikuyaya
- 1587 (如水庵) Taira no An
- 1587 (長五郎餅本舗) Chogoro Mochi Honpo
- 1592 (大杉屋惣兵衛) Oosugi Ya Sohei
- 1592 (翁飴本舗 桔梗屋) Ogami Mochi Honpo Kikyo Ya
- 1596 (大寺餅河合堂) Daishi Mochi Kawai Do
- 1597 (桑名屋) Kuwana Ya
- 1599 (みなとや幽霊子育飴本舗) Minatoya Yuurei Ko Ichiyaki Honpo
Hotels and Ryokan
- 705 (西山温泉慶雲館 ) - Nishiyama Onsen Keiun-kan
- 717 (千年の湯 古まん) - Sennen no yu furuman
- 718 (善吾楼) - Zen'gōrō
- 1075 (雪国の宿 高半) - Yukiguni no yado Takahashi
- 1134 (夏油温泉) - Natsu-abura Onsen
- 1184 (ホテル佐勘) - Hotel Sankan
- 1191 (有馬温泉 奥の坊) - Arima Onsen Okuno-bō
- 1191 (陶泉 御所坊) - Tōzen Gosho-bō
- 1192 (よしのや依緑園) - Yoshinoya Iridō-en
- 1311 (のとや) - Noto-ya
- 1312 (東屋旅館 ) - Tōya Ryokan
- 1428 (佐久ホテル) - Saku Hotel
- 1428 (湯主一條) - Yunagi-no-yado
- 1502 (千明仁泉亭) - Sennō Jinsen-tei
- 1536 (和泉屋旅館 (栃木県)) - Izumi-ya Ryokan Tochigi-ken
- 1546 (湯元 不忘閣) - Yugen Fubō-kaku
- 1551 (板室温泉大黒屋) - Itamuro Onsen Daikokuyama-ya
- 1560 (時音の宿 湯主一條) - Toki-ne no yado Yunagi-no-yado
- 1561 (山県館) - Yama-ken-kan
- 1563 (四万たむら ) - Shimantamura
- 1576 (岸権旅館) - Kishi Ken Ryokan
- 1578 (ランプの宿) - Lamp no Yu
- 1591 (ホテル木暮) - Hotel Kimokaze
- 1596 (湯守 玉林房) - Yumori Tama Rinbo
- 1599 (爽神堂七山病院) - Soushindo Nanzan Byouin
- 1599 (草津温泉 望雲) - Kusatsu Onsen Moongaze
- 1600 (古久屋) - Furuya
Sake factory and sale
- 1141 (須藤本家) - Sudō Honke
- 1487 (飛良泉本舗) - Hira-izumi Manpō
- 1505 (剣菱酒造) - Ken-shō-shuzō
- 1532 (山路酒造) - Yamaji Shuzō
- 1534 (冨田酒造) - Tomita Shuzō
- 1540(酒千蔵野) - Sake Sen-no-no
- 1548 (吉乃川) - Yoshinogawa
- 1550 (小西酒造) - Konishi Shuzō
- 1558 (上田酒造) - Ueda Shuzō
- 1592 (名門サカイ) - Meimon Sakai
- 1593 (小屋酒造) - Koya Sakezou
- 1596 (豊島屋本店) - Toshima Ya Honten
- 1597 (龍神酒造) - Ryujin Sakezou
- 1597 (小島醸造) - Kojima Jozou
- 1597 (小嶋総本店) - Kojima Sohonten
Pharmaceutical industry
- 1319 (三光丸) - Sankō- maru
- 1368 (ういろう) - Uiro
- 1570 (伊勢くすり本舗) - Ise Kusuri- honpo
- 1579 (中屋彦十郎薬舗) - Nakaya Hikojuro Yakuhin
- 1597 (宇津救命丸) - Utsu Kyuumeiwan
- 1598 (和歌の浦井本薬房) - Waka no Urai Honyakufu
- 1600 (川又薬局) - Kawamatsu Yakkyoku
Others
- 578 (金剛組) - Kongō- gumi - construction industry
- 771 (源田紙業) - Motoda Kami- gyō - Manufacture of paper boxes
- 885 (田中伊雅仏具店 ) - Tanaka Ima Hōgu- ten - accessories for Buddhist altars
- 970 (中村社寺) - Nakamura- sha- ji - construction industry
- 1024 (朱宮神仏具店) - Shukyō Hōgu- ten - accessories for Buddhist altars
- 1160 (通圓) - Tsūen - tea making
- 1184 (菊岡漢方薬局) - Kikuka kanpō- yaku- kyoku - Pharmacy trade
- 1189 (伊藤鉄工) - Itō Tetsu- kō - Foundry → + Machining → Machining [55]
- 1337 (まるや八丁味噌) - Maruya Hachidō- miso - miso
- 1346 (高田装束) - Takada Sōzoku - clothing manufacturing
- 1392 (松前屋) - Matsumae- ya - Seafood
- 1395 (鉛市) - Namiji - chemical industry
- 1462 (センキヤ) - Senkiya - tea making
- 1465 (本家尾張屋) - Honke Owari- ya - Restaurant
- 1501 (復古堂) - Fukkō- dō - brush making
- 1534 (松岡屋醸造場) - Matsuoka- ya Jōzō- jō - Manufacture of fermented foods
- 1547 (国友久太郎商店) - Kuniyuki Kyūtarō- shōten - manufacture of gunpowder
- 1550 (紋屋井関) - Monoya Isuke - Obi production
- 1554 (名エン) - Meien - salt industry
- 1555 (千切屋治兵衛) - Chigiri- ya Jirōbei- shōten - Kimono manufactures wholesale
- 1555 (千總) - Chizō - clothing manufacturing
- 1558 (懐古堂) - Kaiko- dō - Painting
- 1559 (上林春松本店) - Urayama Shunshō- motenari- ten - tea making
- 1560 (ナベヤ (企業)) - Nabe- ya (kigyō) - Metal processing industry
- 1560 (岡本 (鋳物)) - Okamoto (chūmoku) - steel industry
- 1560 (戸谷八商店) - Toya Hachiman- shōten - sale of pottery
- 1560 (有次) - Ari- tsu - kitchen knives
- 1560 (長谷木) - Haseki - office rental business
- 1563 (糀屋 (群馬県)) - Kōya (Gunma- ken) - miso
- 1566 (西川) - Nishikawa - bed linen
- 1568 (吉字屋本店) - Yoshizawa Honten - oil industry
- 1572 (吉田源之丞老舗) - Yoshida Gen- nōjō- rō- ten - accessories for Buddhist altars
- 1573 (ナカノ) - Nakano - fresh fish wholesale
- 1573 (上田五兵衛商店) - Ueda Gobei- shōten - chemical industry
- 1573 (大津屋) - Ōtsu- ya - convenience store
- 1573 (室次) - Muro- tsu - production of soy sauce
- 1573 (細字印判店) - Sosozō- inpanto- ten - production of stamps
- 1575 (濱田屋・ジャパン) - Hama- da- ya Japan - Painting
- 1575 (目細八郎兵衛商店) - Mehosiro- hachirōbei- shōten - making hair needles
- 1576 (山ばな平八茶屋) - Yamabana Heihachaya - Restaurant
- 1577 (古梅園) - Kumeen - ink manufacturing
- 1577 (湊與) - Minato Yo - fresh fish wholesale
- 1578 (とみひろ) - Tomihiro - Kimono manufactures wholesale
- 1579 (木倉や) - Kikura Ya - Kimono
- 1580 (ヒガシマル醤油) - Higashimaru Shoyu - production of soy sauce
- 1582 (印傳屋) - Inchuan Ya - leather industry
- 1582 (尾道造酢) - Omote Zou - production of vinegar
- 1582 (波多野塗料) - Hatanono Nuriya - manufacture of paints
- 1582 (田丸屋) - Tamawarya Straw shoes shop
- 1582 (箕輪漆行) - Minowa Shikko - Painting
- 1582 (香十) - Kouju - manufacture of incense
- 1584 (ヤマトインテック) - Yamato Intec - Metal processing industry
- 1584 (ゑり善) - Eri Zen - clothing manufacturing
- 1585 (メルクロス) - Merukurosu - daily needs
- 1585 (茶の天正園) - Cha no Tenseien - tea making
- 1586 (小山社寺工業所) - Koyama Shotenkougyousho - construction work
- 1586 (松井建設) - Matsui Kensetsu - construction industry
- 1587 (礒野産業) - Isono Sangyou - real estate business
- 1588 (オケカ厨熱) - Okeka Chukanetsu - Equipment construction company
- 1590 (伊場仙) - Iba Sen - Fans
- 1590 (住友グループ) - Sumitomo Group - Mining *Currently a business group
- 1591 (山科 (広島県)) - Yamasha (Hiroshima Prefecture) - household goods
- 1592 (祢ざめ家) - Nizameya - Restaurant
- 1593 (山本屋種苗店) - Yamamoto Ya Shumokuten - Manufacture and sale of seedlings
- 1594 (薫玉堂) - Kaori Tama Do - manufacture of incense
- 1594 (藤野屋商店) - Fujiya Shouten – Manufacture and sale of fertilizers
- 1596 (タキモ商店) - Takimo Shouten - food wholesale
- 1596 (タゼン) - Tazen - Gas equipment
- 1596 (元祖丁子屋) - Ganso Chingoya - Restaurant
- 1598 (中里茂右エ門窯) - Nakazato Shigeuemon Kama - pottery manufacturing
- 1598 (沈寿官窯) - Shinju Kan - pottery manufacturing
- 1598 (綿半グループ) - Watanoha Group - construction industry
- 1599 (京林) - Kyōrin - Kimono
- 1599 (爽神堂七山病院) - Soushindo Nanzan Byouin - hospital
- 1599 (馬居化成工業) - Maike Kassei Kogyo - chemical industry
- 1600 (木村新造装束店) - Kimura Shinsouzoku Shukuten - clothing manufacturing