Chess originated from a game called Chaturanga in China. While most of the world plays traditional chess, Japan and some Asian countries have their own version of chess. The Japanese version is called Shogi (将棋). In this article, we'll learn how to play this fun and strategic chess game.
They say the shogi was introduced to Japan in the Nara period (704 to 790 AD). If so, then it is possible that shogi has no origins in chaturanga or Chinese chess. There is a notable difference between them. The objective of the game is the same as in western chess, "capture the opponent's king". But the pieces and the board change.

Índice de Conteúdo
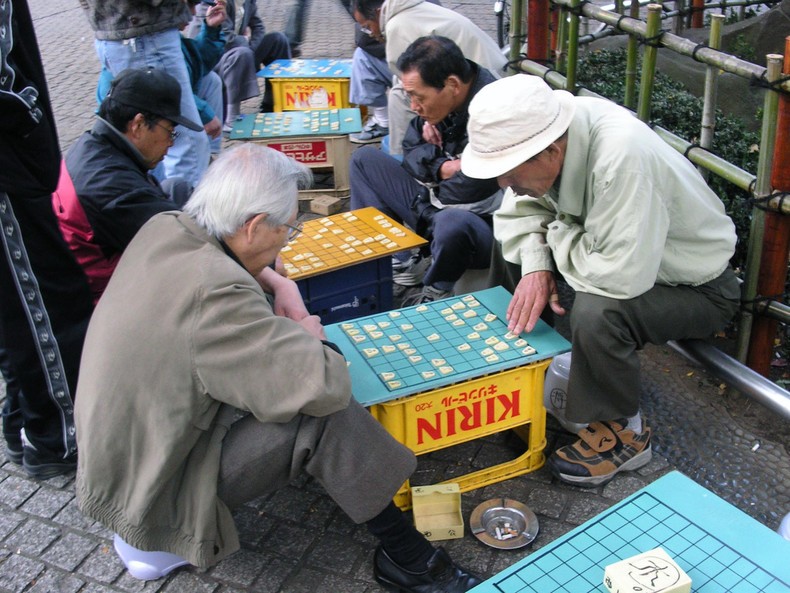
Japanese chess pieces
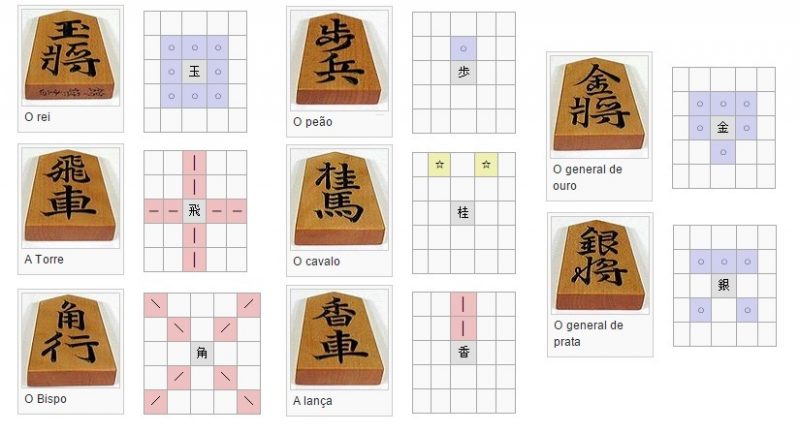
Japanese chess is played on a 9-row by 9-column board. Each player has 20 pieces equal to the other player. One player's pieces are distinguished from those of another by the direction they point on the board.
The game has equal pieces on both teams to work the capture and return system in the game. Also, some parts have drawings on both parts to identify when a part was promoted. The 20 pieces are as follows:
- 1 king
- 2 golden generals
- 2 silver generals
- 2 horses
- 2 spearmen
- 1 bishop
- 1 tower
- 9 pawns
Japanese chess moves
According to the image below you can see all the movements of the pieces in the shogi, and see how similar they are to Western Chess.
Japanese chess promotion
who arrive at promotion zone you can choose to promote your piece which will give you new moves.
- The silver general, knight, spear, or pawn assumes the move of a gold general
- The rook or bishop in addition to its normal movement gains one more move. One square diagonally in the case of the rook and one square horizontally or vertically in the case of the bishop;
The image below shows the promotion zone and movement, and the starting position plus the kanji of each piece:
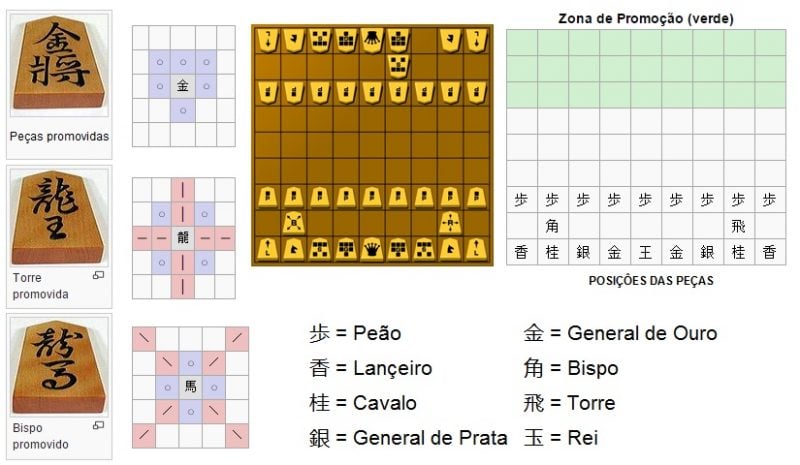
When a piece reaches the last three lines it may or may not be promoted. The decision is at the player's discretion. He has the opportunity to choose whether or not to promote his pieces every time he moves them around these squares. If the spearman, knight or pawn reaches the last row, promotion becomes mandatory.
All pieces when promoted become a gold general, with the exception of the bishop, rook, and the gold general itself. The bishop, in addition to its normal movement, gains the right to move one square vertically or horizontally. The rook, in addition to its normal movement, gains the right to move one square diagonally. The golden General cannot be promoted.
The article is still halfway through, but we recommend also reading:
Capture in Japanese Chess
Unlike chess, in Shogi we don't eat pieces, but capture. A captured piece is kept in the hand and can be brought back into the game under the control of the player who captured it (replacement), that is, it becomes part of that player's army as a kind of reserve (but without the promotion). In the title below, the rules for replacing the pieces.
If a king accidentally enters a piece's line of attack, it can be captured and the game is over.
Replacement of parts
Instead of making a normal move, a player can choose one of the pieces he has captured and replace it (without the promotion) on the board as his own piece. Rules:
- The piece must be placed in an empty house (that is, it cannot be placed and capture another piece) from anywhere on the board (as long as it does not fall under the following restrictions), even in the promotion zone, but promotion is not immediate (promotion can occur normally in subsequent moves);
- A piece cannot be placed on a square from which it could not make a legal move (pawns, spears and knights on the last line, nor knights on the penultimate);
- A pawn cannot be placed on a column that already contains another unpromoted pawn from the same player (“nifu”). If a player already has an unpromoted pawn on each file, he cannot replace a pawn anywhere; for this reason, it is common to sacrifice a pawn in order to gain flexibility for replacement;
- When replacing a pawn, it is not allowed to checkmate (“uchifuzume”), but it can give a check. Other pieces can give immediate checkmate when they are replaced;
- A game is won by checkmating the opponent's king. Due to the rule of reintroduction of pieces, a stalemate (which would mean a draw) is highly unlikely.
- The perpetual check is prohibited. The player who causes such a situation is obliged to abandon it;
- The repositioning capability of Shogi gives the game tactical richness and complexity;
Download Shogi
If you are interested in playing shogi, you can download an application for your Smartphone or Tablet, or play online or download it on your computer.
- Click here to access shogi games on the Play Store
- Click here to play Shogi Online
- Click here to play Online in Flash
- Shogi on IOS - IPHONE
Hope you enjoyed the article! We count on your possible sharing!






